Restoration
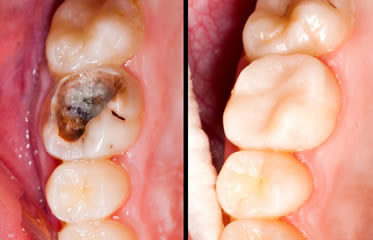 A dental restoration or dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the physical integrity of the intended restorative material.
A dental restoration or dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the aesthetics or the physical integrity of the intended restorative material.
Dental Restorations can be divided broadly into direct and indirect restorations.
- Direct Restorations
This technique involves placing a soft or malleable filling into the prepared tooth and building up the tooth before the material sets hard. The advantage of direct restorations is that they usually set quickly and can be placed in a single procedure. Various types of filling materials are available and the choice of material is based upon the extent of caries, age and other factors. Tooth colored materials called composites is the most popular of the materials available. - Indirect Restorations
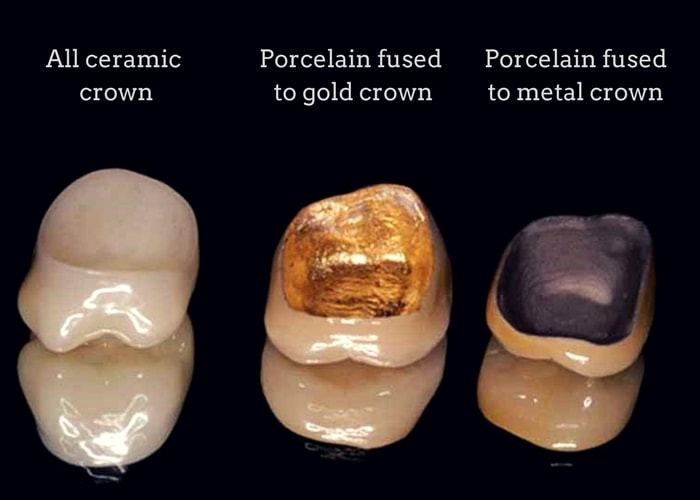

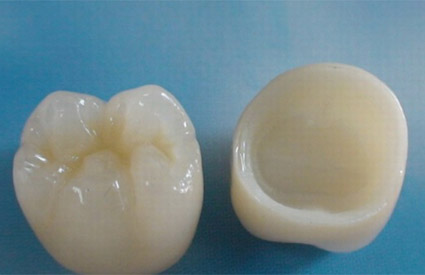 In this technique the restoration is fabricated outside of the mouth using the dental impressions of the prepared tooth. Common indirect restorations include inlays and onlays, crowns, bridges, and veneers. Usually a dental technician fabricates the indirect restoration from records the dentist has provided of the prepared tooth. The finished restoration is usually bonded permanently with a dental cement. It is often done in two separate visits to the dentist. The restoration could be fabricated in complete porcelain or their fusion with a metal alloy or precious metals like gold.
In this technique the restoration is fabricated outside of the mouth using the dental impressions of the prepared tooth. Common indirect restorations include inlays and onlays, crowns, bridges, and veneers. Usually a dental technician fabricates the indirect restoration from records the dentist has provided of the prepared tooth. The finished restoration is usually bonded permanently with a dental cement. It is often done in two separate visits to the dentist. The restoration could be fabricated in complete porcelain or their fusion with a metal alloy or precious metals like gold.
Opening Hours
- Mon to Sat -
10:30am - 06:30 pm
- Sunday Closed